- This topic is empty.
-
AuthorPosts
-
2025-08-06 at 6:03 pm #86051
Pimelic acid, chemically known as heptanedioic acid, plays a vital role in organic synthesis and polymer chemistry. As a seven-carbon dicarboxylic acid, it serves as a critical intermediate in the synthesis of polyamides, notably nylon-66, and various other industrial and pharmaceutical applications. In this blog post, SACH, a high purity microbial synthesized chemicals manufacturer, will share the role of key intermediate pimelic acid for nylon-66 organic synthesis.
1. Chemical Profile of Pimelic Acid
* Chemical Name: Pimelic acid
* CAS Number: 111-16-0
* EC Number: 203-840-8
* Molecular Formula: C₇H₁₂O₄
* Molecular Weight: 160.17 g/mol
* Appearance: White to slightly beige powder
* Melting Point: 103–105 °C (lit.)
* Boiling Point: 212 °C at 10 mmHg (lit.)
* Purity: ≥99%
* Packaging: 25 kg/drum
* Storage Conditions: Store below +30°C in a dry, well-ventilated environment
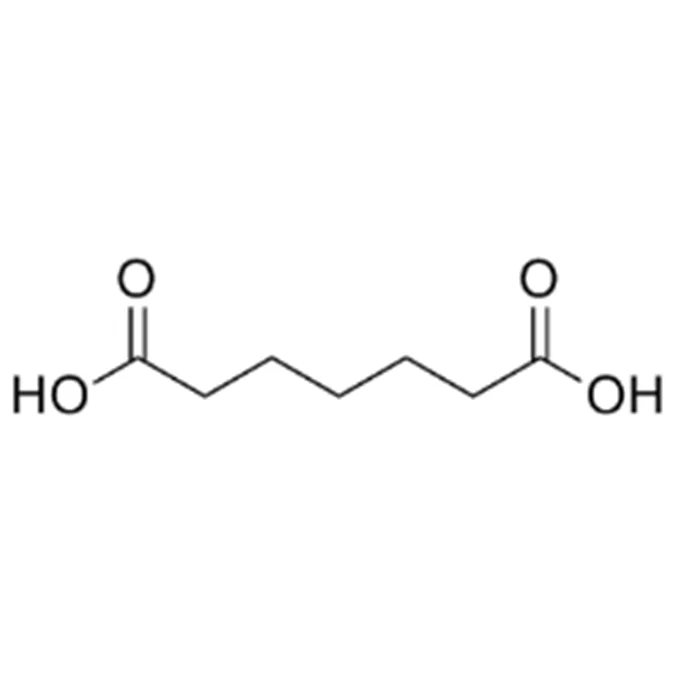
Pimelic acid is part of the α,ω-dicarboxylic acid family, featuring two terminal carboxyl groups separated by five methylene units. Its molecular structure imparts unique reactivity in condensation reactions and polymer formation.
2. Synthesis and Industrial Production
Pimelic acid can be produced via several chemical routes. The classical method involves the oxidation of cycloheptanone or hydrogenation of aromatic precursors. Advances in catalytic processes now enable more efficient and environmentally friendly production methods.
2.1 Oxidation of Cycloheptanone
This process includes the oxidation of cycloheptanone using nitric acid or other oxidants under controlled temperature and pressure to yield pimelic acid with high purity.
2.2 Biotechnological Approaches
Biological production using engineered microorganisms is emerging as a sustainable alternative. This method utilizes renewable feedstocks and genetically modified microbes capable of converting sugars to pimelic acid under fermentation conditions.
3. Pimelic Acid in Nylon-66 Synthesis
While nylon-66 is traditionally made from adipic acid (C6) and hexamethylenediamine, pimelic acid serves as a valuable alternative or modifier in the production of specialty polyamides.
3.1 Structural Compatibility
As a dicarboxylic acid, pimelic acid reacts with diamines to form long-chain polyamides. Its seven-carbon backbone (C7) introduces subtle variations in polymer flexibility, thermal resistance, and crystallinity, compared to conventional adipic acid.
3.2 Nylon Variants and Copolymers
Pimelic acid is often used in the formation of co-polymers or modified nylons such as:
* Nylon 7,6 (pimelic acid + hexamethylenediamine)
* Co-polyamides for enhanced elasticity and moisture absorption
These modified nylons are widely used in textiles, engineering plastics, and automotive components requiring tailored mechanical and thermal properties.
4. Role in Organic and Medicinal Chemistry
Beyond nylon production, pimelic acid is a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of:
* Plasticizers
* Lubricants
* Corrosion inhibitors
* Pharmaceuticals
4.1 Enzyme Inhibitor Synthesis
Pimelic acid has been employed as a starting material in the preparation of enzyme inhibitors, especially those targeting biotin-dependent carboxylases, due to its structural similarity to biotin derivatives.
4.2 Functional Group Transformations
Its two reactive carboxylic groups allow for easy derivatization into esters, amides, or anhydrides, facilitating its incorporation into complex organic frameworks.
5. Physical and Handling Properties
The substance is a stable crystalline powder, slightly hygroscopic, and must be handled in accordance with standard chemical safety procedures.
5.1 Stability
Pimelic acid is stable under standard conditions but may decompose under excessive heat or strong oxidizing environments. It should be stored in sealed containers, away from light and moisture.
5.2 Transport and Packaging
Commercially supplied in 25 kg fiber drums or HDPE containers, it is classified as non-hazardous for transport but should be managed using appropriate PPE (gloves, goggles, dust mask) during handling.
6. Environmental and Safety Considerations
Pimelic acid is considered low in toxicity and is biodegradable. However, spills or improper disposal may lead to environmental concerns due to local pH disruptions from acidic properties.
* Toxicity: Low oral and dermal toxicity
* Biodegradability: Readily biodegradable
* Disposal: Follow local regulations; avoid release into sewage systems or natural water sources.
7. Market Applications and Demand Outlook
As industries seek performance-driven materials with enhanced durability, the demand for specialty nylons incorporating pimelic acid is expected to grow.
7.1 Application Industries
* Textile industry: Elastic and resilient synthetic fibers
* Automotive sector: Heat-resistant polyamide parts
* Consumer goods: Durable nylon components
* Medical field: Bio-compatible polymers
7.2 Competitive Advantages
Compared with shorter-chain analogs like adipic acid, pimelic acid imparts increased chain length, improved flexibility, and better thermal stability to polymers, making it ideal for next-generation engineering plastics.
Conclusion
Pimelic acid is more than just a specialty dicarboxylic acid—it is a cornerstone for innovations in nylon synthesis and organic chemistry. Its unique seven-carbon chain structure enables the development of advanced materials that balance performance and processability. With continued research into sustainable synthesis and new polymer applications, pimelic acid will remain a key intermediate in modern industrial chemistry.
-
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.


